Review 3 - Codesign Challenge, FPGA-SoC
Codesign Challenge
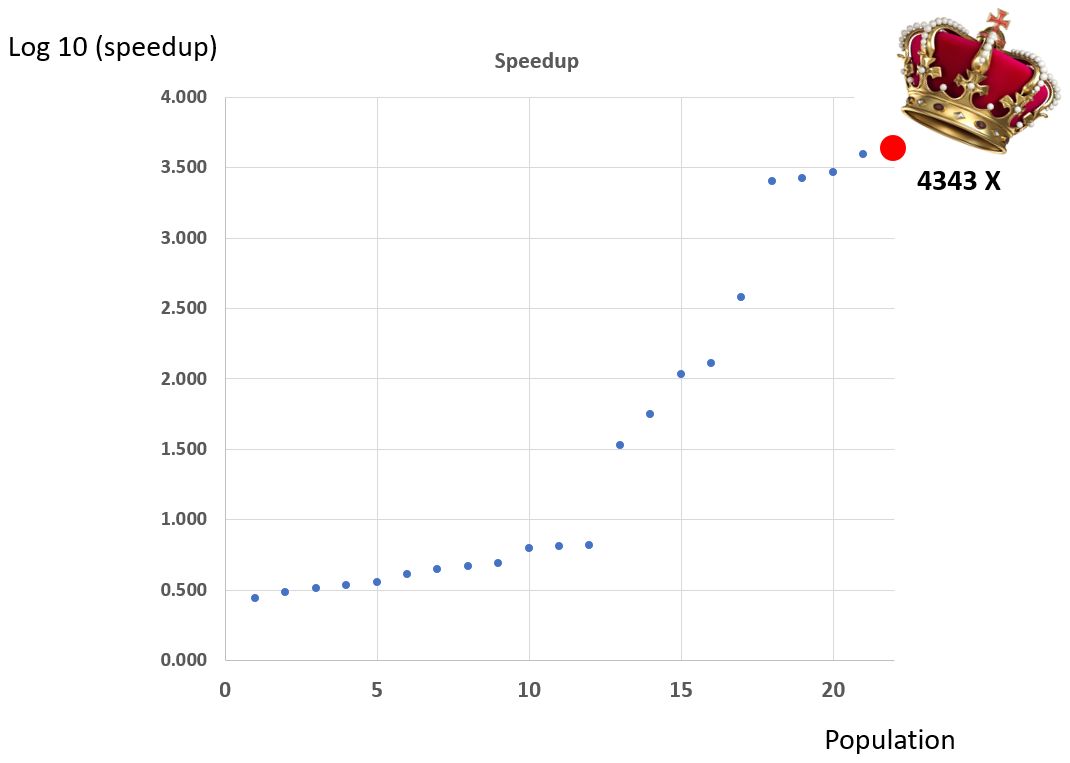
The outcome of the codesign challenge, in terms of speedup, is demonstrated below.
Study Guide
The final exam covers Lecture 16 to 22 included. In the final few lectures, we spend more time in thinking about system design, and how to support a systematic acceleration strategy. We discussed the role of analysis of control flow and data flow, and the role of profiling and debugging.
-
Lecture 16 - FPGA-SoC
- Differences between HPS, Nios, and MSP430 in various aspects including memory hierarchy, interconnect, processor capabilities.
- Virtual Memory
- Impact of an operating system on the hardware/software interface (as opposed to ‘bare metal’ design)
-
Lecture 17 - FPGA SoC 2
- Memory map of the HPS system; integration of FPGA resources
- Difference between swap mempory region and virtual memory; effect of allocating variables in a program on the available virtual memory
- Example: Integration of the I2C device driver
- Example: Programming of the I2C based accelerometer
- Performance evaluation (pitfalls)
-
Lecture 18 - Control Flow and Data Flow
- Meaning of data flow edge and control flow edge
- Construction of the control flow graph
- Mapping a C program (trivially) to hardware using CD/DF analysis
-
Lecture 19 - Debugging and Profiling
- Principle operation of gdb
- Principle operation of gprof
- Interpretation of the output of gprof (function profile and call tree profile)
-
Lecture 20 - Cordic Coprocessor
- Operation of the CORDIC algorithm
- Fixed point arithmetic
- Custom-instruction Interface for CORDIC
- How to control variable placement in (embedded) memory
-
Lecture 21 - Codesign Challenge
- Basic optimization of a nested loop by propagating constant values
- Basic optimization techniques for floating point operations
-
Lecture 22 - Codesign Challenge 2
- Principle of Direct Memory Access (DMA)
- Principle of a multiply-accumulate coprocessor